knee joint
Knee joint injuries and diseases are a common problem among adults, leading to pain, discomfort, and disability. The knee joint is one of the most used and abused joints in the body, and as such is prone to a variety of injuries and diseases.
The most common type of knee injury is an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear. This often occurs when the knee is twisted or bent abnormally and can affect anyone, regardless of age or activity level. ACL tears can lead to pain, swelling, and difficulty walking or running. Treatment typically involves physical therapy, bracing, and in some cases, surgery. Another common knee injury is a meniscal tear. Meniscal tears occur when the meniscus, a cushion between the thigh and shin bones, becomes torn or damaged. Symptoms of a meniscal tear include pain and swelling. Treatment includes physical therapy, bracing, and in some cases surgery.
Degenerative joint diseases of the knee, such as osteoarthritis, are also common. Osteoarthritis is a condition that occurs when the cartilage that cushions the knee joint wears away, leading to stiffness, pain, and swelling. Treatment for osteoarthritis includes physical therapy
knee anatomy basics
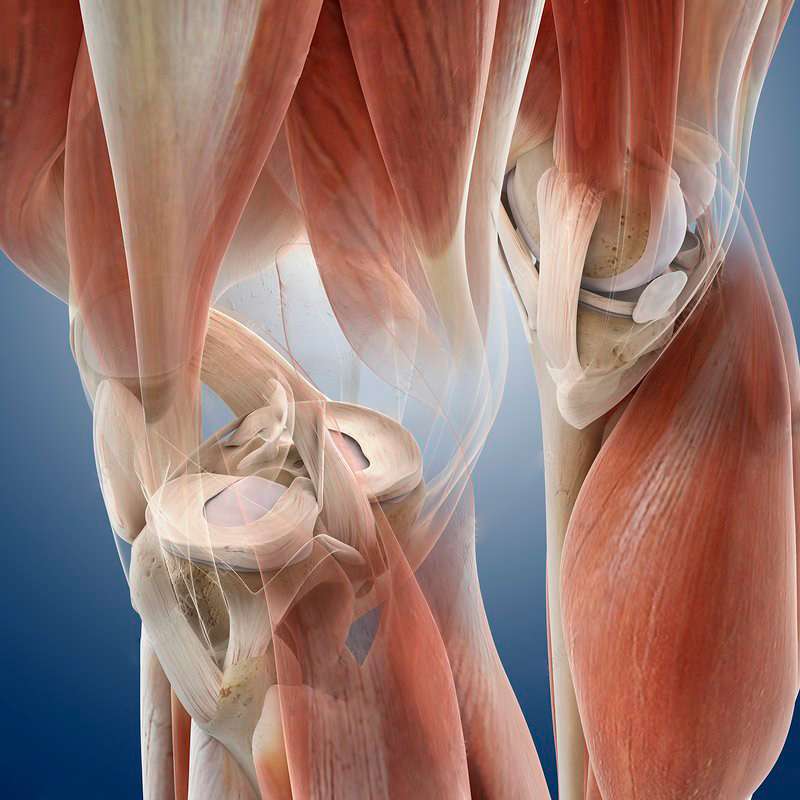
The knee joint is made up of three main bones: the femur, the tibia, and the patella (knee cap). The femur and tibia are connected by two main ligaments: the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and the lateral collateral ligament (LCL). The MCL is located on the inner side of the knee, and the LCL is located on the outer side of the knee.
The knee joint is also surrounded by several muscles, including the quadriceps muscles (located on the front of the thigh) and the hamstrings muscles (located on the back of the thigh). These muscles help to move and stabilize the knee joint.
The knee joint is cushioned by two small discs of cartilage called the menisci (plural of meniscus). The menisci help to distribute weight across the joint and protect the bones from rubbing against each other.
The knee joint is also surrounded by a joint capsule, which is a sac of connective tissue that encloses the joint and helps to lubricate and protect it. The joint capsule is filled with a thick, clear fluid called synovial fluid, which helps to lubricate the joint and reduce friction.
common sports injuries of knee joint
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury: The ACL is a ligament that runs from the front of the tibia to the back of the femur and helps to stabilize the knee joint. Meniscal tear: The menisci are two small discs of cartilage located in the knee joint. A meniscal tear can occur when the knee is twisted or bent in an awkward position, such as when making a sudden cut or pivot during sports. Symptoms of a meniscal tear may include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee.
The menisci are two small discs of cartilage located in the knee joint. They act as shock absorbers and help to distribute weight across the joint. A meniscus tear is a tear in one or both of these discs. It is a common sports injury, particularly in sports that involve twisting or turning the knee, such as soccer, basketball, and football.
Symptoms of a meniscus tear may include:
- Pain in the knee, especially when twisting or turning
- Swelling in the knee
- Stiffness in the knee
- Difficulty straightening or fully extending the knee
- A feeling of the knee “catching” or “locking”
Meniscus tears are usually diagnosed through a physical examination and imaging tests, such as an MRI. Treatment for a meniscus tear may include rest, ice, physical therapy, and surgery. In some cases, a meniscus tear may be able to heal on its own with rest and physical therapy. In other cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove the damaged tissue.
Recovery from a meniscus tear can take several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the tear and the treatment. After recovery, it is important to engage in a program of strengthening and balance exercises to help prevent future injuries.
Fracture: A fracture is a break in one of the bones of the knee. It can occur as a result of a direct blow to the knee or from falling and landing on the knee. Symptoms of a fracture may include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee.
Recurrent Patella Dislocation: A dislocation occurs when the bones of the knee joint become displaced from their normal positions. It can occur as a result of a direct blow to the knee or from falling and landing on the knee. Symptoms of a dislocation may include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee. Patellar dislocation occurs when the patella (knee cap) becomes displaced from its normal position in the patellofemoral groove (a depression on the femur). This can cause pain, instability, and difficulty moving the knee. Patellar dislocations are often caused by a direct blow to the knee, a fall, or a sudden change in direction.
Recurrent patellar dislocation refers to multiple dislocations of the patella. This can occur when the patella is unstable and prone to becoming dislocated. Recurrent patellar dislocations can be caused by a variety of factors, such as ligamentous laxity (loose ligaments), muscle weakness, and structural abnormalities of the knee joint.
Symptoms of a recurrent patellar dislocation may include:
- Pain in the knee, especially when moving the leg
- Swelling or tenderness in the knee
- Instability or “giving way” of the knee
- A feeling of the patella “moving out of place”
Treatment for recurrent patellar dislocation may include physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, bracing to stabilize the patella, and surgery to repair any structural abnormalities or tighten loose ligaments. The specific treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the recurrent dislocations and the patient’s symptoms.
Patellar tendonitis: Patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, is an inflammation of the patellar tendon, which connects the patella (knee cap) to the tibia. It is often caused by repetitive strain on the tendon, such as from jumping or running. Symptoms of patellar tendonitis may include pain, swelling, and difficulty extending the leg.
Bursitis: Bursitis is an inflammation of a bursa (a small fluid-filled sac) in the knee. It can be caused by repetitive strain or overuse of the bursa. Symptoms of bursitis may include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee
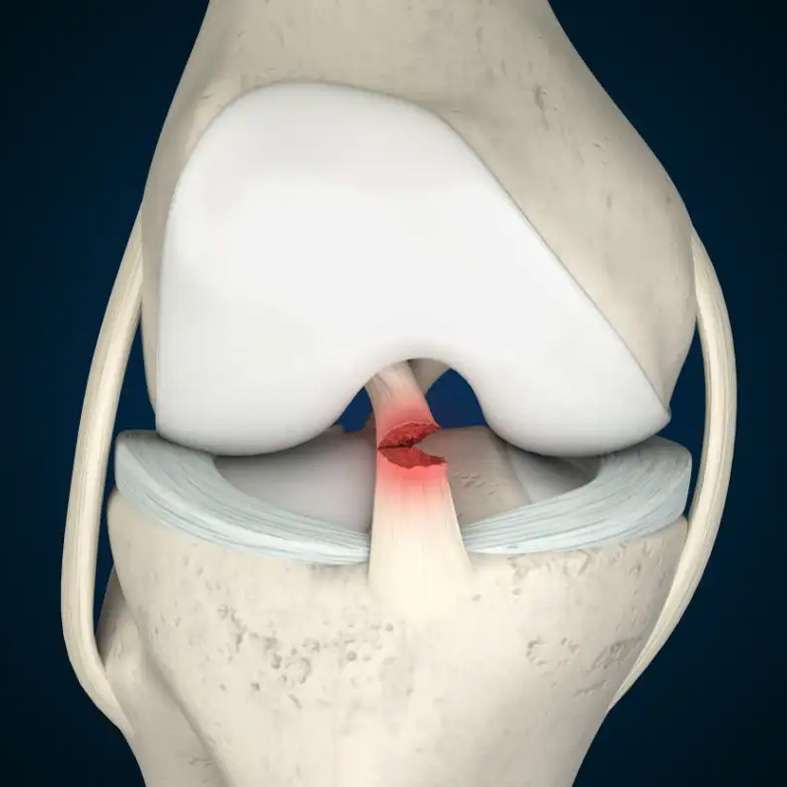
Anterior cruciate ligament tear of knee
-
An ACL injury can occur when the knee is twisted or bent in an awkward position, such as when making a sudden cut or pivot during sports. Symptoms of an ACL injury may include pain, swelling, and instability in the knee. It is a common sports injury, particularly in sports that involve cutting, pivoting, or sudden changes in direction.
Symptoms of an ACL tear may include:
- Pain, swelling, and tenderness in the knee
- Instability or “giving way” of the knee
- A feeling of the knee “moving out of place”
- A popping sensation at the time of the injury
ACL tears are usually diagnosed through a physical examination and imaging tests, such as an MRI. Treatment for an ACL tear may include rest, ice, physical therapy, and surgery. Surgery is typically recommended for athletes and other active individuals who wish to return to high-impact sports, as it can help to restore stability to the knee joint.
Recovery from an ACL tear can take several months and may require a significant amount of physical therapy. After recovery, it is important to engage in a program of strengthening and balance exercises to help prevent future injuries.
osteoarthritis knee
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes the cartilage in the joint to wear away. When it affects the knee, it is known as knee osteoarthritis. Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that can cause pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving the knee. It is more common in people who are older, overweight, or have had a previous knee injury.
Knee osteoarthritis is often graded on a scale from 0 to 4, with 0 being normal and 4 being severe:
- Grade 0: Normal
- Grade 1: Mild osteoarthritis with some loss of cartilage
- Grade 2: Moderate osteoarthritis with significant loss of cartilage
- Grade 3: Severe osteoarthritis with severe loss of cartilage
- Grade 4: Very severe osteoarthritis with complete loss of cartilage
Treatment for knee osteoarthritis may include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
- Physical therapy to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion
- Weight loss to reduce stress on the knee joint
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation
- Hyaluronic acid injections to lubricate the knee joint
- Total knee replacement surgery to replace the damaged joint with an artificial one
Knee arthroscopy
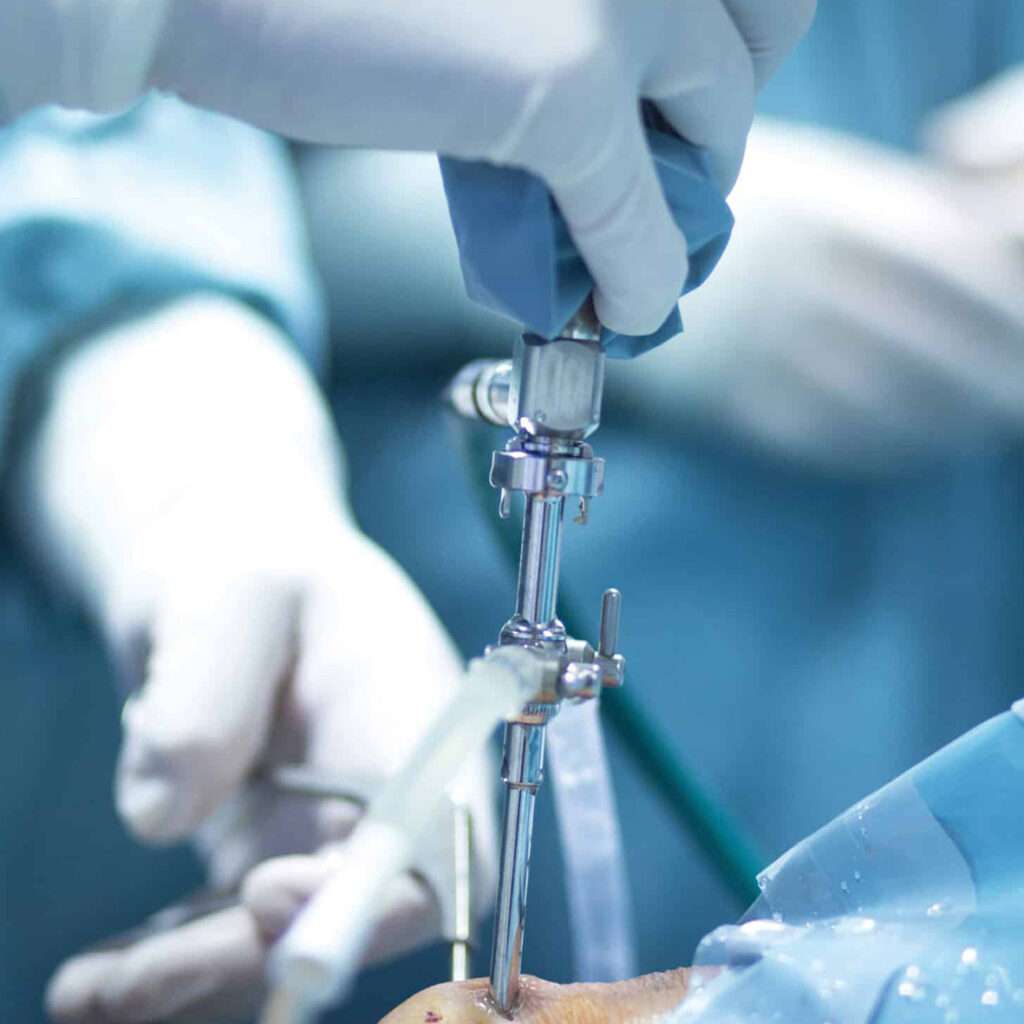
Knee arthroscopy is a surgical procedure in which a small camera (arthroscope) is inserted into the knee joint through a small incision. The arthroscope allows the surgeon to see inside the joint and diagnose or treat various conditions.
Indications for knee arthroscopy may include:
- Meniscal tear
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear
- Articular cartilage injury
- Osteoarthritis
- Patellar subluxation or dislocation
- Synovitis (inflammation of the synovial membrane)
During the procedure, the patient will be placed under general or regional anesthesia. Small incisions will be made around the knee joint, and the arthroscope will be inserted through one of these incisions. The surgeon will use the arthroscope to visualize the inside of the joint and diagnose or treat the condition.
Complications of knee arthroscopy may include infection, bleeding, nerve or blood vessel injury, and stiffness or limited range of motion in the knee joint.
